The Rise of Plant-Based Diets: Health and Sustainability Benefits
In recent years, plant-based diets have gained tremendous popularity, driven by a growing awareness of health benefits, environmental concerns, and animal welfare considerations. The rise of plant-based eating represents a significant shift in how people approach their diet, moving away from animal-based products towards a more sustainable and health-conscious lifestyle. This detailed guide explores the rise of plant-based diets, the health benefits, sustainability advantages, and how you can make the switch to plant-based eating.
What is a Plant-Based Diet?
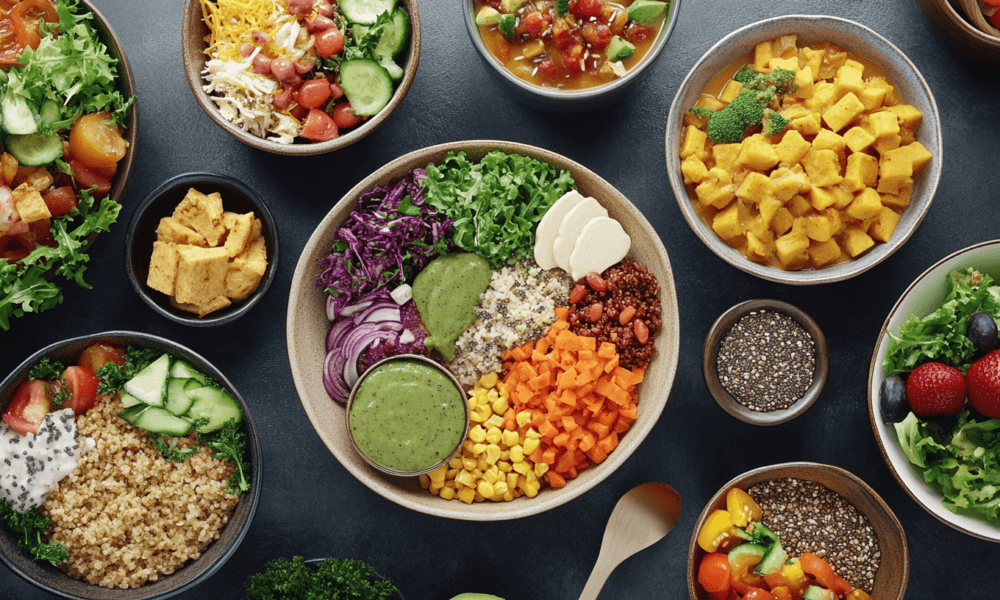
A plant-based diet focuses on foods derived from plants, including fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. While many people associate plant-based diets with veganism, it doesn’t necessarily mean eliminating all animal products. Instead, plant-based eating prioritizes plant-derived foods and minimizes animal-based products. This diet can range from fully vegan to vegetarian, or even flexitarian, where occasional consumption of animal products is allowed.
Types of Plant-Based Diets
- Vegan Diet: Completely excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey.
- Vegetarian Diet: Eliminates meat, poultry, and fish but includes dairy and eggs.
- Flexitarian Diet: Primarily plant-based but allows for occasional consumption of meat and other animal products.
- Pescatarian Diet: Plant-based with the inclusion of fish and seafood.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets are often associated with a wide range of health benefits. By prioritizing nutrient-rich plant foods, individuals can significantly improve their overall health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and enhance their well-being.
1. Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains has been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Heart Health: Plant-based diets are associated with lower cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and improved heart health. The high fiber content and lack of saturated fat in plant-based foods help maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes Management: A diet high in plant-based foods can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it an effective approach to managing type 2 diabetes. Whole grains, legumes, and vegetables have a low glycemic index, which helps maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Cancer Prevention: Many studies suggest that plant-based diets are linked to a lower risk of certain cancers, particularly colorectal and breast cancers. The high levels of antioxidants, fiber, and phytochemicals found in plant-based foods contribute to this reduced risk.
2. Weight Management
Plant-based diets are often effective for weight loss and weight management. By focusing on whole, minimally processed foods that are naturally lower in calories and higher in fiber, individuals can feel fuller for longer and avoid overeating.
- High Fiber Content: Plant-based foods are typically high in dietary fiber, which helps regulate appetite, improves digestion, and contributes to weight loss.
- Lower Caloric Density: Fruits, vegetables, and legumes are less calorie-dense than many animal-based foods, allowing individuals to consume larger portions without consuming excess calories.
3. Improved Gut Health
A plant-based diet promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in overall health. The fiber in plant-based foods feeds beneficial gut bacteria, promoting better digestion and reducing inflammation.
- Diverse Gut Microbiome: A diverse range of plant foods supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is linked to improved immunity, mental health, and digestion.
- Reduced Inflammation: Fiber-rich foods and the absence of inflammatory compounds found in some animal products can help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
The rise of plant-based diets is not only motivated by health considerations but also by the growing awareness of environmental and sustainability issues. The production of plant-based foods has a significantly lower environmental impact compared to animal agriculture, making plant-based diets a key component of sustainable living.
1. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Animal agriculture is one of the leading contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Livestock production releases large amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. By reducing or eliminating animal products, individuals can significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Producing plant-based foods generates fewer greenhouse gases compared to meat and dairy production. For example, producing one kilogram of beef produces significantly more emissions compared to the same amount of legumes or vegetables.
- Mitigating Climate Change: By adopting plant-based diets, individuals can help mitigate climate change by reducing emissions associated with livestock farming.
2. Conservation of Water Resources
Animal agriculture is highly water-intensive, requiring large amounts of water for livestock and feed production. By contrast, plant-based foods typically require much less water to produce.
- Water Savings: It takes significantly less water to grow crops like grains, legumes, and vegetables compared to raising livestock. For example, producing one kilogram of beef requires approximately 15,000 liters of water, while producing one kilogram of lentils requires only about 1,250 liters.
- Drought Mitigation: By reducing water consumption, plant-based diets can help mitigate the impact of droughts and water shortages in vulnerable regions.
3. Preservation of Natural Habitats
The expansion of livestock farming often leads to deforestation and habitat destruction, threatening wildlife and biodiversity. Adopting plant-based diets can help preserve natural habitats and protect endangered species.
- Reduced Deforestation: Livestock farming is a major driver of deforestation, particularly in regions like the Amazon rainforest. By reducing demand for animal products, plant-based diets can help reduce the need for land conversion.
- Biodiversity Protection: Preserving natural habitats supports biodiversity, helping protect various plant and animal species from extinction.
How to Transition to a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By making gradual changes and incorporating more plant-based foods into your meals, you can enjoy the health and sustainability benefits of this lifestyle.
1. Start Small and Set Goals
- Meatless Mondays: Start by eliminating meat from your diet one day a week. Meatless Mondays are a great way to introduce plant-based meals into your routine without feeling overwhelmed.
- Gradual Reduction: Gradually reduce your intake of animal products over time. For example, replace cow’s milk with almond or oat milk, or swap beef burgers for plant-based alternatives.
2. Focus on Whole Foods
- Fruits and Vegetables: Incorporate a wide variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet to ensure you are getting essential vitamins and minerals.
- Legumes and Whole Grains: Beans, lentils, quinoa, and brown rice are nutrient-dense and rich in protein and fiber, making them great staples for a plant-based diet.
3. Experiment with Plant-Based Proteins
Protein is an essential nutrient, and there are plenty of plant-based sources that can meet your protein needs.
- Tofu and Tempeh: Both tofu and tempeh are versatile and rich in protein, making them ideal substitutes for meat in stir-fries, curries, and other dishes.
- Legumes: Chickpeas, black beans, and lentils are excellent sources of protein and can be used in soups, salads, and stews.
- Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Many plant-based meat alternatives, such as those from brands like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, provide the texture and flavor of meat without the environmental impact.
4. Plan Balanced Meals
To ensure that you are meeting your nutritional needs, plan balanced meals that include a variety of food groups.
- Include Protein, Carbs, and Fats: Each meal should contain a source of protein (e.g., beans, tofu), carbohydrates (e.g., quinoa, sweet potatoes), and healthy fats (e.g., avocados, nuts).
- Don’t Forget Nutritional Supplements: Depending on your diet, you may need supplements for nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can be harder to obtain from plant-based foods.
Common Myths About Plant-Based Diets
Despite the growing popularity of plant-based diets, there are still several myths and misconceptions that can deter people from making the switch. Here, we debunk some common myths about plant-based diets:
1. Myth: Plant-Based Diets Lack Protein
One of the most common myths is that plant-based diets do not provide enough protein. In reality, there are numerous plant-based sources of protein, including legumes, nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, and whole grains.
2. Myth: Plant-Based Diets Are Expensive
While some plant-based meat substitutes can be costly, plant-based diets can be affordable, especially when focusing on whole foods like beans, lentils, rice, and vegetables.
3. Myth: Plant-Based Diets Are Boring
Plant-based diets can be incredibly diverse and flavorful. With so many plant-based recipes available, there are endless ways to enjoy delicious and satisfying meals.
Conclusion
The rise of plant-based diets is a positive trend that offers numerous health and sustainability benefits. By reducing the consumption of animal products and focusing on nutrient-rich plant foods, individuals can improve their health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and contribute to a more sustainable planet. Whether you choose to go fully vegan, vegetarian, or simply incorporate more plant-based meals into your diet, every step counts towards a healthier future for both yourself and the environment.



No Comment! Be the first one.