Telehealth 2.0: Expanding Access to Healthcare Through Virtual Care and Remote Monitoring
The world of healthcare is undergoing a significant transformation, and at the heart of this change is the evolution of telehealth. With the advent of new technologies and the challenges brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has rapidly expanded, offering more ways than ever for patients to connect with healthcare professionals without visiting a traditional medical facility. Now, we are witnessing the next phase: Telehealth 2.0, which goes beyond simple video consultations to include comprehensive virtual care and remote monitoring solutions. This revolution in healthcare is reshaping how care is delivered, making it more accessible, convenient, and patient-centered. In this article, we will explore how Telehealth 2.0 is transforming healthcare, its benefits, challenges, and what it means for the future of medicine.
What is Telehealth 2.0?
Telehealth 2.0 is the next generation of virtual healthcare services that encompass not only video consultations but also advanced remote monitoring, digital therapeutics, and integrated patient management systems. It represents a shift from traditional, episodic care to continuous, proactive, and patient-centered care that can be delivered anywhere, at any time.
Components of Telehealth 2.0
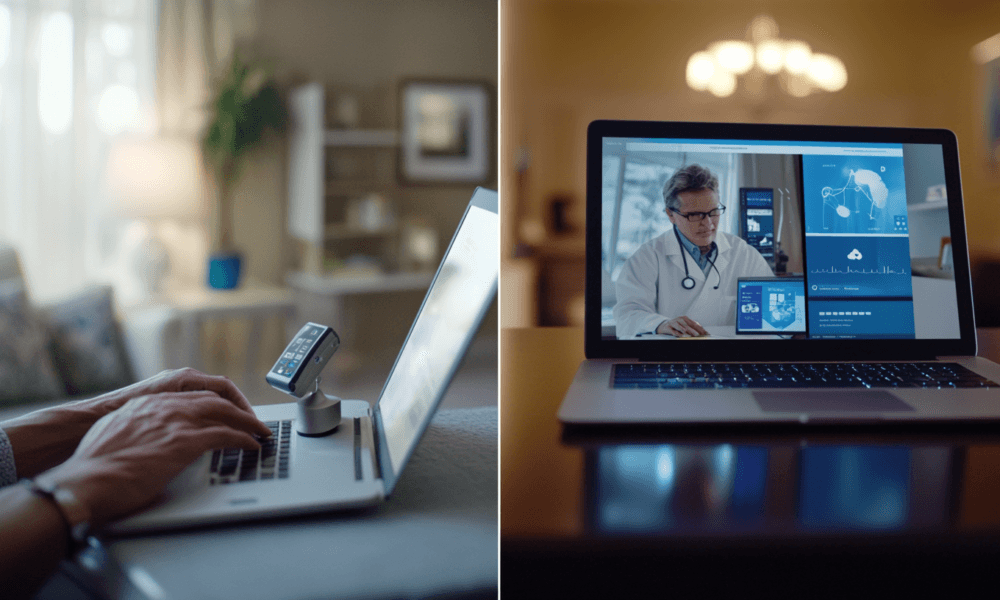
- Virtual Care: This includes live video consultations, chat-based communications, and asynchronous care (store-and-forward technologies). Patients can consult with healthcare providers through mobile devices, laptops, or tablets from the comfort of their homes.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Remote monitoring uses connected medical devices to collect health data from patients in real time. This data is then transmitted to healthcare professionals, who can monitor patient health remotely and make informed decisions.
- Digital Therapeutics: These are evidence-based interventions delivered via software that help manage or treat medical conditions. Examples include mobile apps for managing diabetes, mental health, or sleep disorders.
- Integrated Patient Management: Telehealth 2.0 integrates with electronic health records (EHRs), ensuring that healthcare providers have access to a complete view of a patient’s medical history, allowing for better decision-making.
Benefits of Telehealth 2.0
Telehealth 2.0 offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers, enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and quality of care. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Improved Access to Care
One of the most significant benefits of Telehealth 2.0 is that it expands access to healthcare services, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas. By providing virtual care options, patients can receive timely medical attention without the need to travel long distances.
- Rural and Remote Areas: Telehealth 2.0 ensures that patients in rural or remote areas can connect with specialists and receive care that may not be available locally.
- Chronic Condition Management: Patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, can benefit from remote monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to track their progress and intervene when necessary.
2. Enhanced Patient Engagement
Telehealth 2.0 empowers patients to take a more active role in their health. Remote monitoring devices and digital health apps provide patients with real-time insights into their health metrics, encouraging them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment.
- Health Data at Fingertips: Patients can track vital signs, such as blood pressure or glucose levels, through connected devices, giving them greater awareness of their health.
- Proactive Care: By involving patients in their own care, telehealth promotes proactive behavior, such as adhering to medication schedules or following treatment plans.
3. Cost Savings
Telehealth can lead to significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems. By reducing the need for in-person visits, telehealth minimizes travel expenses, time off work, and other costs associated with traditional healthcare.
- Reduced Hospital Readmissions: Remote monitoring allows for early detection of potential health issues, reducing the likelihood of hospital readmissions and the associated costs.
- Lower Overhead for Providers: Healthcare providers can lower overhead costs by reducing the need for physical office space and resources, particularly for follow-up visits and routine consultations.
4. Convenience and Flexibility
With virtual care and remote monitoring, patients can receive care when and where they need it. This level of convenience is particularly beneficial for patients with mobility issues, those with busy schedules, or caregivers who need flexibility.
- Flexible Scheduling: Patients can schedule virtual visits at times that work for them, often with shorter waiting times than in-person visits.
- Home-Based Care: Remote monitoring allows patients to receive care from home, reducing the need for frequent visits to the doctor’s office or hospital.
Technologies Driving Telehealth 2.0
Telehealth 2.0 is made possible by a combination of advanced technologies that facilitate virtual care and remote patient monitoring. These technologies are driving innovation in the healthcare industry, making it more connected and efficient.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized healthcare by connecting medical devices that can collect and transmit data in real time. IoT-enabled medical devices, such as smartwatches, glucose monitors, and blood pressure cuffs, are key components of remote patient monitoring.
- Wearable Devices: Wearables such as fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, physical activity, and more, providing valuable data to healthcare providers.
- Medical Sensors: Connected medical sensors can continuously monitor vital signs, allowing for real-time alerts if any abnormalities are detected.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in Telehealth 2.0 by analyzing health data, identifying trends, and providing predictive insights that can aid in decision-making.
- Data Analysis: AI algorithms analyze data from remote monitoring devices to detect potential health issues early, enabling timely intervention.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide answers to common health questions, assist with appointment scheduling, and support patient self-care.
3. Cloud Computing and Data Integration
Cloud computing enables secure storage and easy access to patient data, ensuring that healthcare providers have real-time access to the information they need to make informed decisions.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Integration with cloud-based EHRs allows healthcare providers to access a comprehensive view of a patient’s health history, enhancing care coordination.
- Data Security: Cloud solutions also offer encryption and security measures to protect patient data, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Telehealth 2.0
While Telehealth 2.0 has numerous benefits, there are also challenges that must be addressed to ensure its successful implementation and widespread adoption.
1. Data Privacy and Security
The increased use of digital technologies in healthcare raises concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive patient information from data breaches is a top priority for healthcare providers.
- Compliance with Regulations: Providers must comply with regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. to ensure patient data is protected.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Strong cybersecurity measures, including encryption, secure authentication, and regular audits, are essential to protect patient data from breaches.
2. Digital Divide
Not all patients have access to the technology or reliable internet connection required for telehealth services, which can create disparities in access to care.
- Access to Devices: Some patients may lack access to smartphones, tablets, or computers needed for virtual care.
- Internet Connectivity: Poor or unreliable internet connections in rural or underserved areas can hinder access to telehealth services.
3. Regulatory and Reimbursement Challenges
The regulatory landscape for telehealth varies across regions, and reimbursement policies for virtual care are still evolving.
- Licensing and Cross-State Practice: In some regions, healthcare providers face licensing restrictions that prevent them from offering telehealth services across state or country borders.
- Insurance Reimbursement: The lack of consistent reimbursement policies for telehealth services can deter healthcare providers from offering virtual care options.
The Future of Telehealth 2.0
Telehealth 2.0 is poised to continue transforming healthcare, providing more accessible, efficient, and personalized care. As technology advances, telehealth will become even more integrated into mainstream healthcare delivery.
1. Integration with Wearable Health Tech
The use of wearable health technology is expected to increase, allowing for continuous health monitoring and real-time data sharing with healthcare providers. This will enable proactive interventions and more personalized care.
2. AI-Driven Healthcare
Artificial intelligence will play an even greater role in Telehealth 2.0, enhancing diagnostics, automating administrative tasks, and enabling predictive care. AI-driven telehealth platforms will offer personalized health recommendations and early warnings about potential health risks.
3. Expansion of Virtual Clinics
Virtual clinics will become more commonplace, providing comprehensive care through virtual consultations, digital prescriptions, and remote monitoring. This will allow patients to receive most of their healthcare needs without visiting a traditional clinic.
4. Better Chronic Disease Management
Telehealth 2.0 will play a vital role in managing chronic diseases. Patients with conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or COPD will benefit from real-time monitoring and data-driven interventions, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
Conclusion
Telehealth 2.0 represents a significant step forward in healthcare delivery, leveraging virtual care, remote monitoring, and advanced technologies to expand access to quality healthcare. By improving patient engagement, enhancing convenience, and reducing costs, Telehealth 2.0 is transforming the healthcare landscape. However, challenges such as data privacy, regulatory issues, and the digital divide must be addressed to ensure equitable access for all patients. As technology continues to advance, Telehealth 2.0 will play a crucial role in providing proactive, patient-centered care that meets the evolving needs of individuals around the world.



No Comment! Be the first one.