Extended Reality in Education: Immersive Learning Tools for the Next Generation
Technology is transforming every aspect of our lives, and education is no exception. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, new methods of teaching and learning are being explored to ensure students are better equipped for the challenges of the future. One of the most exciting advancements in education is the integration of extended reality (XR) technologies. Extended reality, an umbrella term that encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), is redefining how students engage with content and enhancing the overall learning experience. This article will dive deep into the role of extended reality in education, the benefits it offers, the challenges it faces, and how it can shape the future of learning.
What Is Extended Reality?
Extended Reality (XR) is a term used to describe immersive technologies that blend the physical and digital worlds to create interactive environments. XR includes:
- Virtual Reality (VR): A fully immersive experience that takes users into a simulated environment, allowing them to interact with digital objects and scenarios as if they were real.
- Augmented Reality (AR): A technology that overlays digital information onto the physical world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings.
- Mixed Reality (MR): A hybrid of VR and AR that combines elements of both, allowing users to interact with virtual objects that are integrated into the real world.
These immersive technologies are increasingly being used in education to create engaging learning experiences that captivate students and make complex concepts easier to understand.
The Role of Extended Reality in Education
Extended reality has the potential to revolutionize education by making learning more interactive, engaging, and effective. Here are some of the ways in which XR is transforming the educational landscape:
1. Enhancing Engagement and Interactivity
Traditional classroom settings can sometimes struggle to engage students, particularly when dealing with abstract or complex topics. XR changes this dynamic by providing interactive and immersive experiences that make learning fun and engaging.
- Virtual Field Trips: With VR, students can take virtual field trips to historical landmarks, museums, or even other planets without ever leaving the classroom. This immersive experience can help students understand the context of what they are learning.
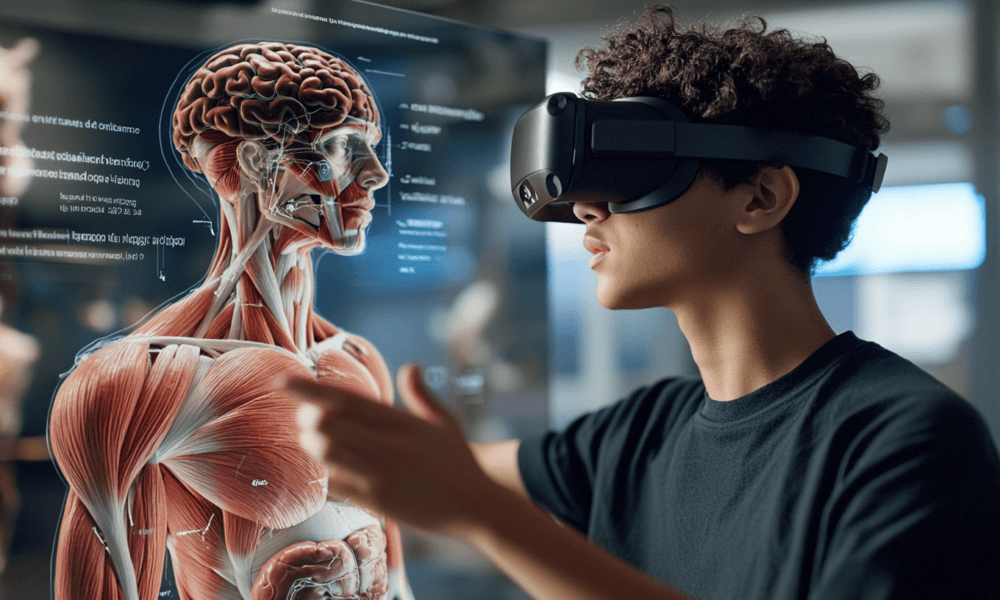
- Interactive Simulations: AR and VR can create simulations that allow students to explore scientific concepts, historical events, and engineering challenges in an interactive way. For example, a biology class could use VR to explore the human body in 3D, giving students a detailed understanding of anatomy.
2. Experiential Learning
Experiential learning—learning by doing—is one of the most effective ways for students to understand and retain information. XR provides a safe and controlled environment for experiential learning, where students can practice skills and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Medical Training: Medical students can use VR to simulate surgeries, allowing them to practice procedures without the risk of harming patients. This helps build their skills and confidence before they enter a clinical setting.
- Technical Training: Students in technical fields like engineering and mechanics can use XR to interact with complex machinery and learn how to repair or operate it. This hands-on experience can make them better prepared for their future careers.
3. Overcoming Learning Barriers
One of the major advantages of XR is its ability to overcome traditional learning barriers and cater to different learning styles.
- Visual and Kinesthetic Learners: Some students learn best through visual or hands-on experiences. XR caters to these learners by providing 3D visuals and interactive environments that make learning more accessible and easier to understand.
- Language and Communication: XR can help bridge language barriers by providing visual cues and interactive simulations that make it easier for students to grasp complex concepts, even if they are not fluent in the language of instruction.
4. Personalized Learning
XR technologies can also facilitate personalized learning by allowing students to learn at their own pace and according to their individual needs. This is particularly important for students who may struggle with traditional classroom instruction.
- Self-Paced Learning: With XR, students can revisit lessons as many times as they need, ensuring they fully understand the material before moving on. This self-paced approach helps build confidence and improves retention.
- Adaptive Content: AR and VR experiences can be tailored to a student’s skill level, ensuring that each learner is challenged appropriately. Adaptive content can help bridge knowledge gaps and provide additional support where needed.
Benefits of Extended Reality in Education
The benefits of using XR in education are numerous, offering both students and educators new ways to teach and learn.
1. Improved Retention and Understanding
Studies have shown that immersive learning experiences can improve knowledge retention. XR allows students to visualize abstract concepts and interact with them in a meaningful way, making it easier to understand and remember the material.
- Active Learning: XR makes learning an active experience, which is known to improve retention compared to passive learning methods like lectures or reading.
- Enhanced Visualization: Complex subjects, such as molecular biology or astrophysics, can be visualized using XR, making it easier for students to understand intricate details.
2. Increased Motivation and Engagement
Students are more motivated to learn when they are actively engaged with the content. XR provides a captivating and fun learning environment that encourages students to participate and explore.
- Gamification: By integrating gamified elements, such as rewards and challenges, XR can make learning more enjoyable and keep students motivated.
- Immersive Storytelling: XR can be used to tell compelling stories that bring historical events or scientific discoveries to life, sparking curiosity and interest in the subject matter.
3. Safe Learning Environment
XR creates a safe and controlled environment where students can experiment and learn without real-world consequences.
- Trial and Error: In XR simulations, students can learn through trial and error without the fear of failure or the risk of causing harm. This encourages them to take risks and explore new ideas.
- Practice for Real-World Situations: For professions that involve risk, such as medicine, firefighting, or engineering, XR provides a realistic environment where students can practice without endangering themselves or others.
Challenges of Implementing Extended Reality in Education
While XR has the potential to revolutionize education, it also comes with its challenges. Addressing these challenges is essential for successful implementation.
1. Cost and Accessibility
One of the biggest challenges of integrating XR in education is the cost of the technology. High-quality VR headsets, AR devices, and content development can be expensive, making it difficult for schools with limited budgets to adopt XR technologies.
- Equipment Costs: VR headsets and AR-enabled devices can be expensive, especially for large classrooms or schools that require multiple units.
- Content Development: Creating engaging and educational XR content requires expertise and resources, which can add to the overall cost.
2. Technical Barriers
The implementation of XR in education requires technical infrastructure, including powerful computers, reliable internet connections, and tech support.
- Hardware Requirements: VR and MR experiences often require high-performance hardware, which may not be readily available in all educational settings.
- Technical Support: Schools may lack the technical expertise needed to set up and maintain XR systems, which could lead to challenges in their day-to-day use.
3. Teacher Training
Educators need to be adequately trained to use XR technologies effectively. Without proper training, teachers may struggle to integrate XR into their lesson plans or may not use it to its full potential.
- Professional Development: Teachers need professional development opportunities to understand how to use XR tools and incorporate them into their curriculum.
- Resistance to Change: Some educators may be resistant to adopting new technologies, especially if they are unfamiliar with XR or unsure of its benefits.
The Future of XR in Education
As XR technologies become more advanced and accessible, their role in education is expected to grow significantly. Here are some of the ways XR could shape the future of learning:
1. Virtual Classrooms and Remote Learning
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of online learning, and XR is poised to take remote education to the next level by creating virtual classrooms where students can interact with each other and their teachers in a more immersive way.
- Virtual Campus Tours: Prospective students can take virtual tours of campuses using VR, allowing them to explore facilities and get a sense of campus life without having to travel.
- Remote Collaboration: XR allows students to collaborate with peers from around the world in a shared virtual space, providing opportunities for cultural exchange and collaborative projects.
2. AI-Driven Personalized Learning
Combining XR with artificial intelligence (AI) could enable more personalized learning experiences that adapt to each student’s needs and learning style.
- Adaptive Learning Paths: AI can analyze a student’s progress and adjust the XR learning experience accordingly, providing extra support where needed and introducing challenges when appropriate.
- Virtual Tutors: AI-driven virtual tutors could guide students through XR experiences, providing real-time feedback and assistance.
3. Lifelong Learning and Skill Development
XR is not limited to K-12 or higher education; it also has applications in lifelong learning and professional development. As the job market evolves, XR can be used to provide on-the-job training and reskilling opportunities.
- Corporate Training: Companies are increasingly using XR for employee training, especially in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. XR provides a hands-on learning experience that is both effective and scalable.
- Continuing Education: XR can make continuing education more engaging for adults, whether they are learning a new language, developing technical skills, or pursuing a personal interest.
Conclusion
Extended reality is transforming education by making learning more immersive, interactive, and effective. By harnessing the power of VR, AR, and MR, educators can create experiences that engage students, improve retention, and cater to diverse learning styles. Despite challenges such as cost and accessibility, the potential benefits of XR in education are immense. As technology continues to advance, extended reality is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of learners, preparing them for the challenges and opportunities of the future.



No Comment! Be the first one.